As the beauty industry raises the bar for quality and precision, the production of synthetic fibers used in products such as eyelashes, makeup brushes, beard brushes, and cleaning brushes has become increasingly critical. This meticulous process involves selecting the right materials, optimizing production techniques, and innovating to meet diverse market needs. In this article, we will take a deep dive into the entire production process of synthetic fibers, covering everything from raw material selection to spinning, cutting, tapering, dyeing, and packaging.
1. Variety in Raw Materials: Choosing the Right Plastic Pellets
The quality of synthetic fibers largely depends on the materials used. Selecting the appropriate plastic pellets is essential, and different materials are chosen based on the desired properties of the fibers. Common materials include:
- PBT (Polybutylene Terephthalate): Known for its flexibility and heat resistance, PBT is ideal for making false eyelashes and makeup brush bristles. It retains its elasticity and shape over extended use.
- PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate): PET is harder and more durable, making it suitable for beard brushes and cleaning brushes, where stiffness is necessary.
- Nylon: This material is highly elastic, anti-static, and resistant to wear, commonly used for makeup brushes like eyebrow and eyeshadow brushes that require precision.
Each material offers distinct physical properties, and the choice of material influences the texture, flexibility, and durability of the finished product.
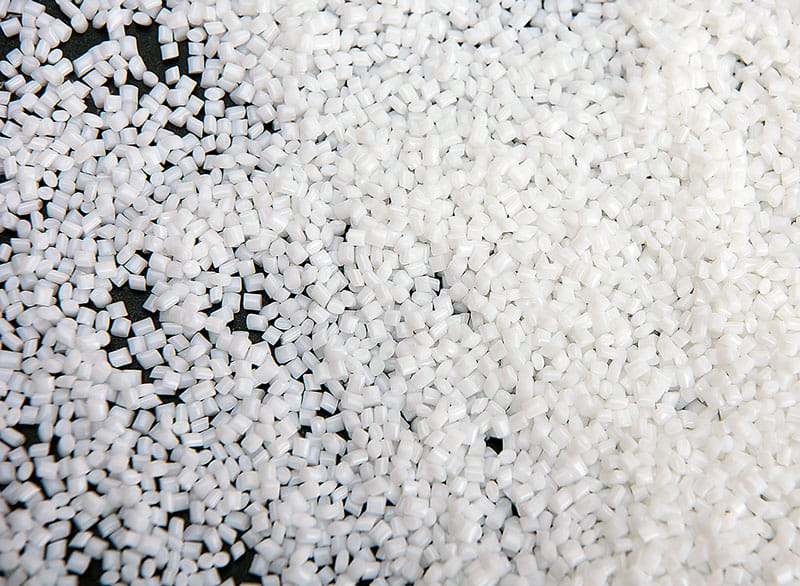

PBT-Granules
2. Functional Additives for Performance Enhancement
To optimize the performance of synthetic fibers, various additives can be incorporated into the plastic pellets. For example:
- Biodegradable additives: As environmental standards tighten, manufacturers are increasingly incorporating biodegradable additives to ensure the fibers can break down in nature, reducing their environmental footprint.
- Anti-static additives: Static electricity can affect the performance of brush bristles, so adding anti-static agents prevents dust and debris from clinging to the fibers, enhancing the user experience.
- Antibacterial additives: For products that come into direct contact with skin, like makeup brushes, antibacterial agents are added to keep the fibers clean and safe, reducing the risk of bacteria buildup.
These additives play an essential role in improving the functionality and marketability of synthetic fibers.
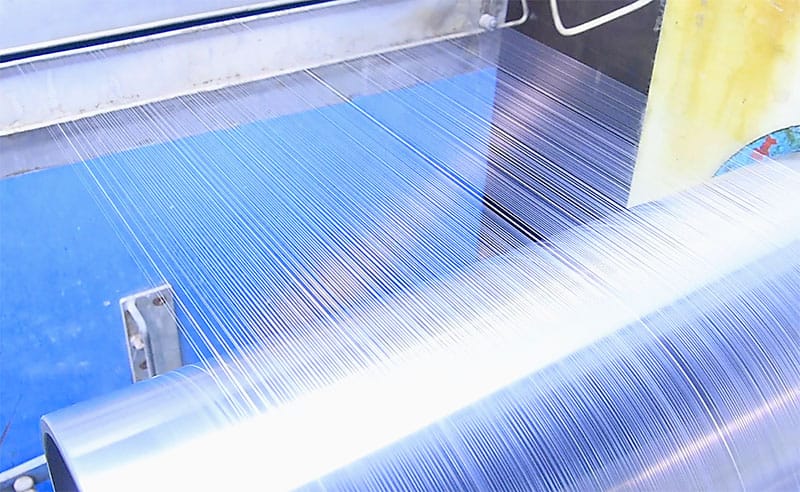
3. The Fiber Spinning Process: From Pellets to Fibers
The production of synthetic fibers starts with spinning, where plastic pellets are melted and drawn into long fibers through a spinning machine.
- Melting and spinning: The plastic pellets are heated to their respective melting points and extruded through spinnerets to form continuous fibers. The temperature and speed of the process must be carefully controlled to produce fibers of uniform diameter. For example, PBT and PET require higher temperatures than nylon to be spun effectively.
- Different molds for varied cross-sections: Depending on the intended application, different molds can be used to create fibers with varying cross-sectional shapes. Circular, triangular, and square cross-sections each impart unique characteristics to the fibers. For instance, triangular fibers offer more precision, making them ideal for tools like eyeliner brushes, while circular fibers are suitable for broader applications like powder brushes.
- Initial cutting and shaping: The fibers are typically cut to an initial length of 1.2 meters after spinning, forming what is known as “fiber spools.” This step is crucial for orderly storage and subsequent processing.
Brushed
4. Tapering the Fiber Tips: Two Key Techniques
After the initial shaping, the fibers undergo a tapering process to refine their tips according to product requirements. There are two primary tapering methods: physical grinding and chemical oxidation.
- Physical grinding: In this method, the fibers are mechanically ground to gradually thin and smooth their tips. This process is often used for makeup brushes, especially powder brushes, where a soft and smooth feel is crucial. Physical grinding ensures the brush bristles are gentle on the skin, providing a luxurious experience.
- Chemical oxidation: Chemical tapering, on the other hand, uses oxidizing agents to treat the fiber tips, resulting in naturally tapered, cone-shaped ends. This method is particularly efficient for producing false eyelashes, where extremely fine and natural-looking tips are required.
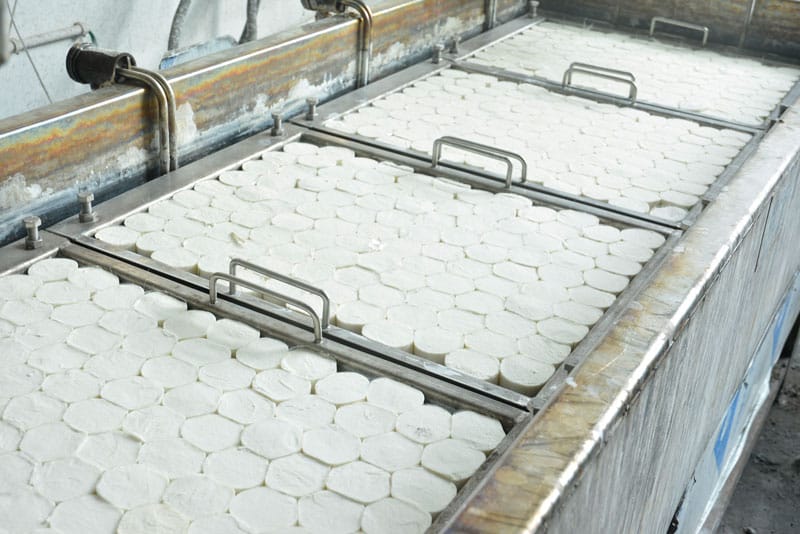

Raw-silk-oxidation
5. Dyeing and Organizing the Fibers
Once the fibers are shaped, they move on to dyeing and organizing processes, where color and structure are added.
- High-temperature dyeing: The fibers are exposed to high temperatures to allow the dye to fully penetrate the material. This ensures that the color remains vibrant and durable. The dyeing process must be carefully controlled to maintain the fibers’ flexibility and strength.
- Machine and manual organization: After dyeing, the fibers are organized mechanically to ensure they are aligned and tangle-free. They are then manually refined to ensure uniformity, especially for high-end products like makeup brushes and eyelashes, where attention to detail is critical.
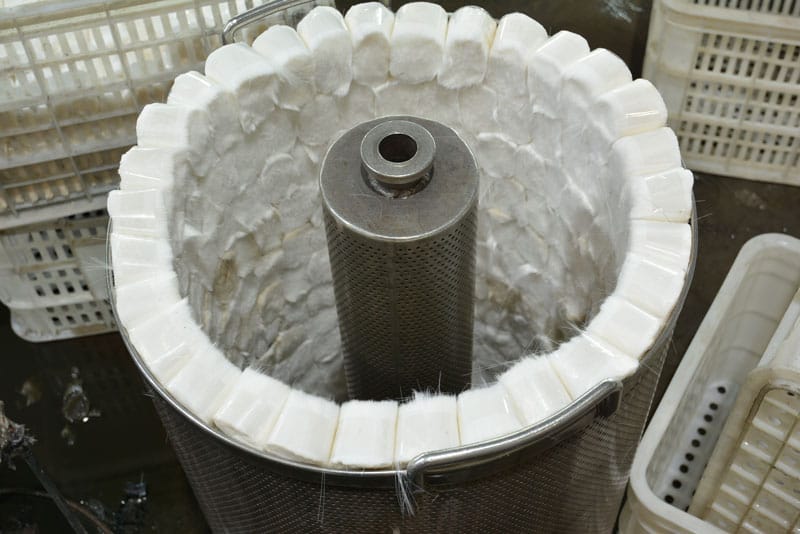

Raw-silk-dyeing
6. Quality Control and Fiber Specifications
Quality control is essential throughout the production process to ensure that the fibers meet the required specifications. Common methods of quality assessment include:
- Precision measurement of diameter and length: Specialized equipment is used to measure the fibers’ diameter and length, ensuring consistency with production standards. For fine brushes and false eyelashes, even the slightest variation can affect the final product’s performance.
- Elasticity and durability testing: The elasticity and durability of the fibers are key performance indicators. Manufacturers conduct tensile and bending tests to ensure the fibers can withstand repeated use without breaking or losing their shape.
- Environmental and safety testing: With increasing awareness of environmental and safety issues, many manufacturers also conduct biodegradability and safety testing to ensure that the fibers are safe for use and environmentally friendly.
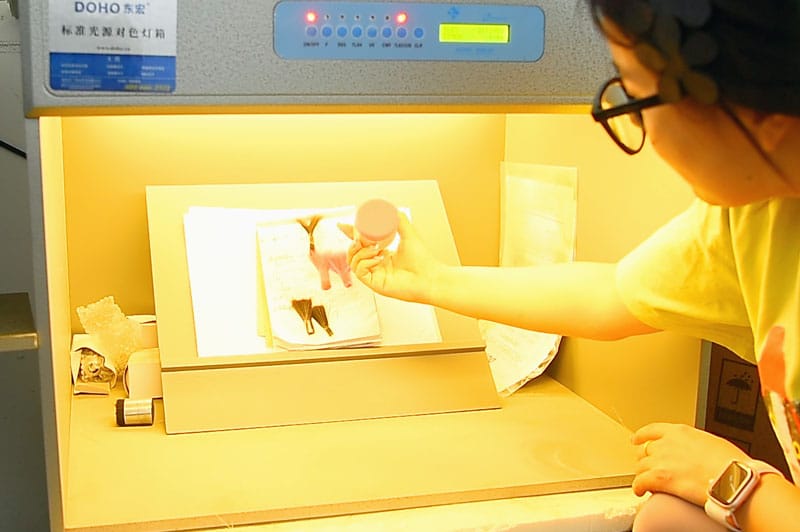

Color calibration
7. Applications and Market Demands
Different types of fibers are tailored for various products, depending on their properties. The characteristics of each fiber—such as material, length, diameter, and cross-sectional shape—determine its ideal application.
- False eyelashes: False eyelashes require ultra-fine, flexible fibers with a natural sheen. PBT or nylon is commonly used due to its elasticity, lightness, and realistic appearance.
- Makeup brushes: The fibers used in makeup brushes vary depending on the brush’s function. Precision tools like eyeshadow and brow brushes require firmer nylon fibers, while softer PBT fibers are used for powder or blush brushes to ensure a smooth application.
- Beard and cleaning brushes: These brushes require sturdier, more durable fibers, typically made from PET. PET’s resilience and toughness make it ideal for products that undergo frequent use and need to maintain their shape.
8. Packaging and Final Processing
After the fibers are processed and inspected, they undergo packaging to ensure they are protected and ready for distribution.
- Protective packaging: Fibers are packaged in materials that prevent moisture, dust, and pressure damage. Each spool or batch of fibers is carefully checked and organized before packaging to ensure it arrives in perfect condition.
- Labeling and classification: Packaging includes detailed labels indicating the fiber material, specifications, batch numbers, and intended uses. Clear labeling helps with tracking, quality control, and ensuring that customers receive the correct product for their needs.
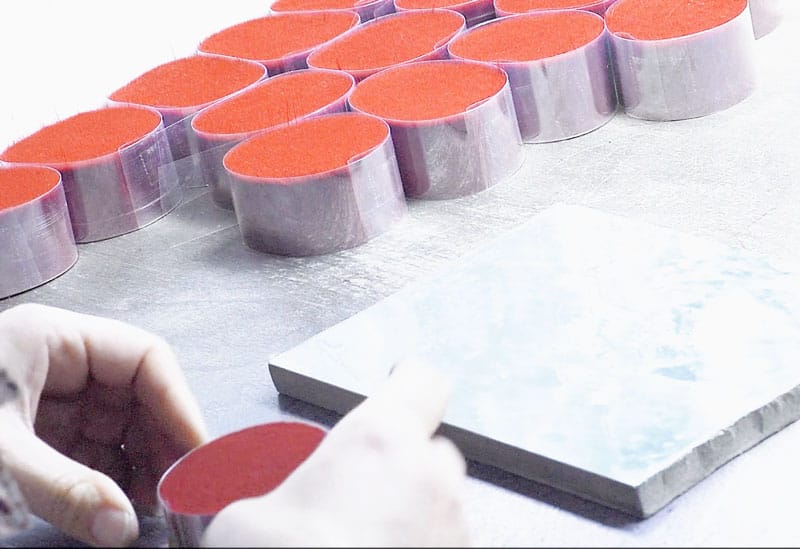

Raw-filament-finishing
9. The Future of Synthetic Fiber Production: Technology and Sustainability
As demand for beauty and household products continues to rise, synthetic fiber manufacturing is evolving rapidly. Future trends in this field focus on two main areas:
- Sustainability: As environmental consciousness grows, there is a push toward using more biodegradable and recyclable materials. The increasing use of PPT and other eco-friendly materials will bring more green solutions to the beauty market.
- Automation and smart production: Advanced spinning machines and tapering technologies will further enhance production efficiency, reducing human errors and boosting consistency. Automated quality control systems will allow for real-time monitoring, ensuring high standards are maintained throughout the manufacturing process.
- Customization and diversification: As consumers demand more personalized products, there will be an increasing need for custom-designed fibers. Different cross-sectional shapes, lengths, and strengths can be tailored to meet specific customer needs, adding more diversity to the product offerings.
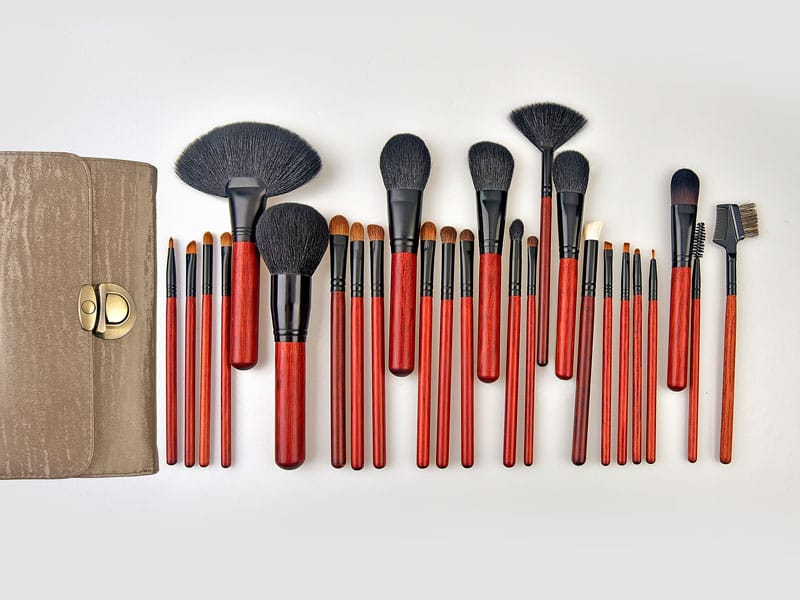

Makeup Brush Set
10. Conclusion: Precision and Innovation in Fiber Production
From raw plastic pellets to finished products, the production of synthetic fibers for eyelashes and brushes involves a highly technical and innovative process. Each step, from material selection to spinning, tapering, and dyeing, is carefully controlled to ensure the highest quality.
Synthetic fiber production is not only a technical feat but also a response to ever-changing market demands. As technology advances and environmental concerns grow, the fiber industry will continue to innovate, providing high-quality raw materials for beauty and household products.





Leave A Comment